Constraints
The Constraints system allows Admin users to configure custom field validation and limitations into IPAM fields. Many constraint types are available, such as mathematical comparison operators, length, enumeration, pre-set lists, RegEx, IPv4/IPv6, Phone, email, hostname, FQDN, Mac Address, and URL.
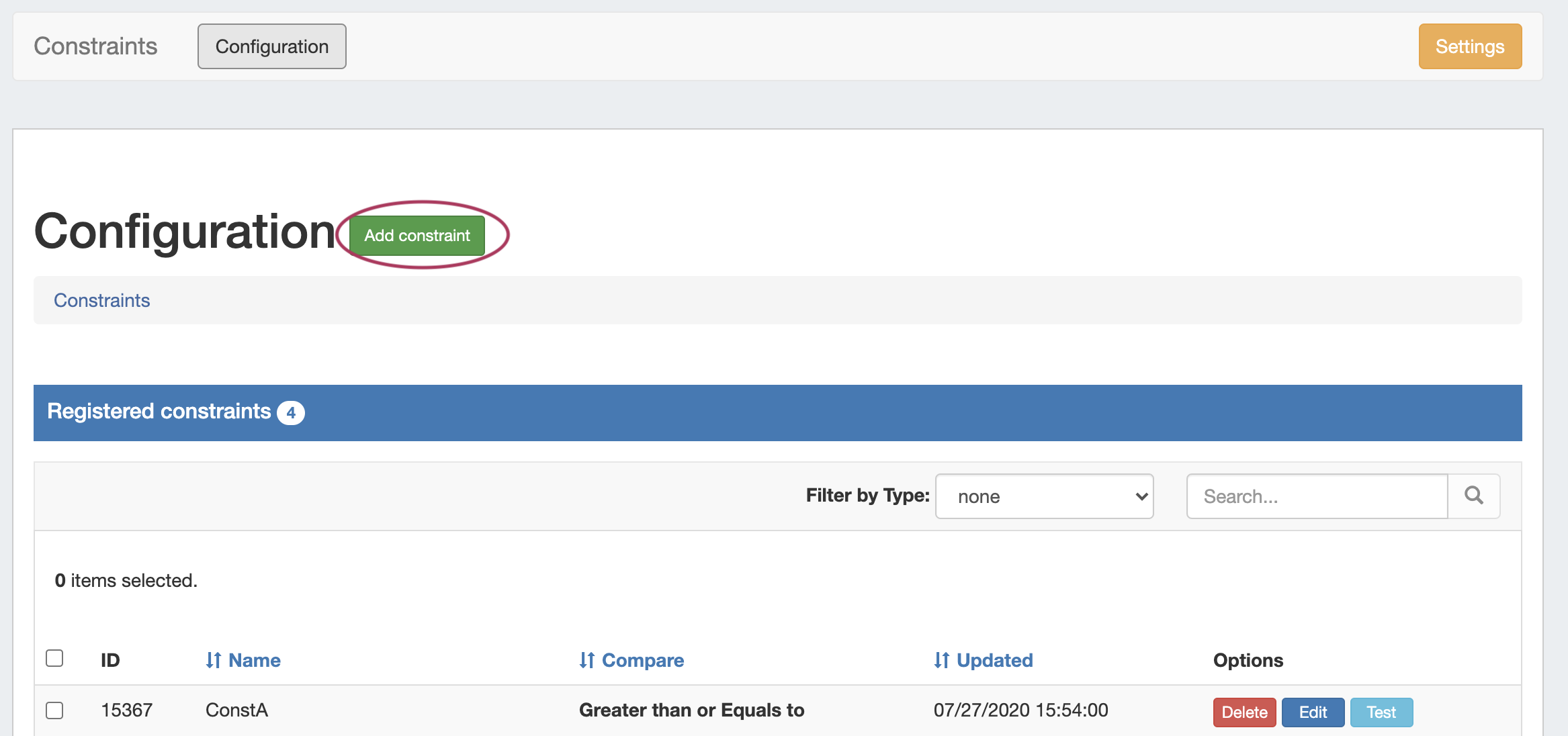
The Constraints Tab has one sub-tab - Configuration - where new constraints may be created and managed.
Currently, Constraints is available only for IPAM related actions, while we gather feedback and use cases to inform possible future updates. If you are interested in providing feedback, a use case, or requests for future additions to the Constraints system, please contact feedback@6connect.com.
Constraints Tab - Overview
The Constraints Tab, available to Admin users, allows for custom field validation and field restrictions to be applied to IPAM fields. The applied constraint may be anything from a numerical comparison operation, a check against a pre-determined text string, ensuring selections from a pre-set list, or forcing entries into a specific format, such as IPv4/IPv6, phone number, or RegEx.
These constraints can be applied to the following IPAM fields:
- ASN
- Custom Generic Field
- Notes
- Metadata 1-10, if enabled for the instance
Depending on the type of constraint applied, the constraint may be a simple single-value comparison needing only one constraint to be created, such as "Equals to" or "Length Max". Some other constraint types, however, may have two or more levels deep of constraint types and value checks. One example of this is "Enumeration", which requires the user to first set up an "Enumeration" constraint, and then a second level list of sub-constraint types or a list of values. For a detailed constraint tree, it may be worth
Available Constraint Types
The following constraint types are currently available:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
Enumeration | Create a list of child enum items. Children type: Valid child enum types are: =, !=, ﹥, ﹤, ﹥=, ﹤=, regex, allow, oneof, allof, ip, ipv4, ipv6, email, url, hostname, fqdn, mac, phone, lenmax, lenmin, section_entry |
| Section Entry | Creates an enumeration based on all entries that belong to a given section. |
| Equals to | Checks to ensure a value is exactly equal to a provided value, e.g. (X == Y) is true |
| Not Equal to | Checks to ensure a value is not equal to a provided value, e.g. (X != Y) is true |
| Greater Than | Checks if the input value (left operand) is greater than a given value (right operand). e.g. (X ﹥ Y) is true |
| Less Than | Checks if the input value (left operand) is less than a given value (right operand). e.g. (X ﹤ Y) is true |
| Greater Than or Equal to | Checks if the input value (left operand) is greater than or equals to a given value (right operand). e.g. (X ﹥= Y) is true |
| Less Than or Equal to | Checks if the input value (left operand) is less than or equals to a given value (right operand). e.g. (X ﹤= Y) is true |
| One of | Create a list of child constraint items. It will be true if one of child constraints is true. Its children must be previously configured. |
| All of | Create a list of child constraint items. It will be true if all of the child constraints are true. Its children must be previously configured. |
| Length Max | Checks to ensure a string has, at most, the specified number of characters |
| Length Min | Checks to ensure a string has, at minimum, the specified number of characters |
| Regular Expression | Compares the input format to a provided Regular Expression |
| IPv4 | Sets the required format for the input to an IPv4 address |
| IPv6 | Sets the required format for the input to an IPv6 address |
| Sets the required format for the input to an email address (uses an "@" symbol) | |
| Hostname | Sets the required format for the input to a hostname. Hostnames may not have underscore or dash characters. |
| FQDN | Sets the required format for the input to a FQDN |
MAC Address | Sets the required format for the input to a MAC address |
| URL | Sets the required format for the input to a url |
| Phone Number | Sets the required format for the input to a phone number |
Add a Constraint
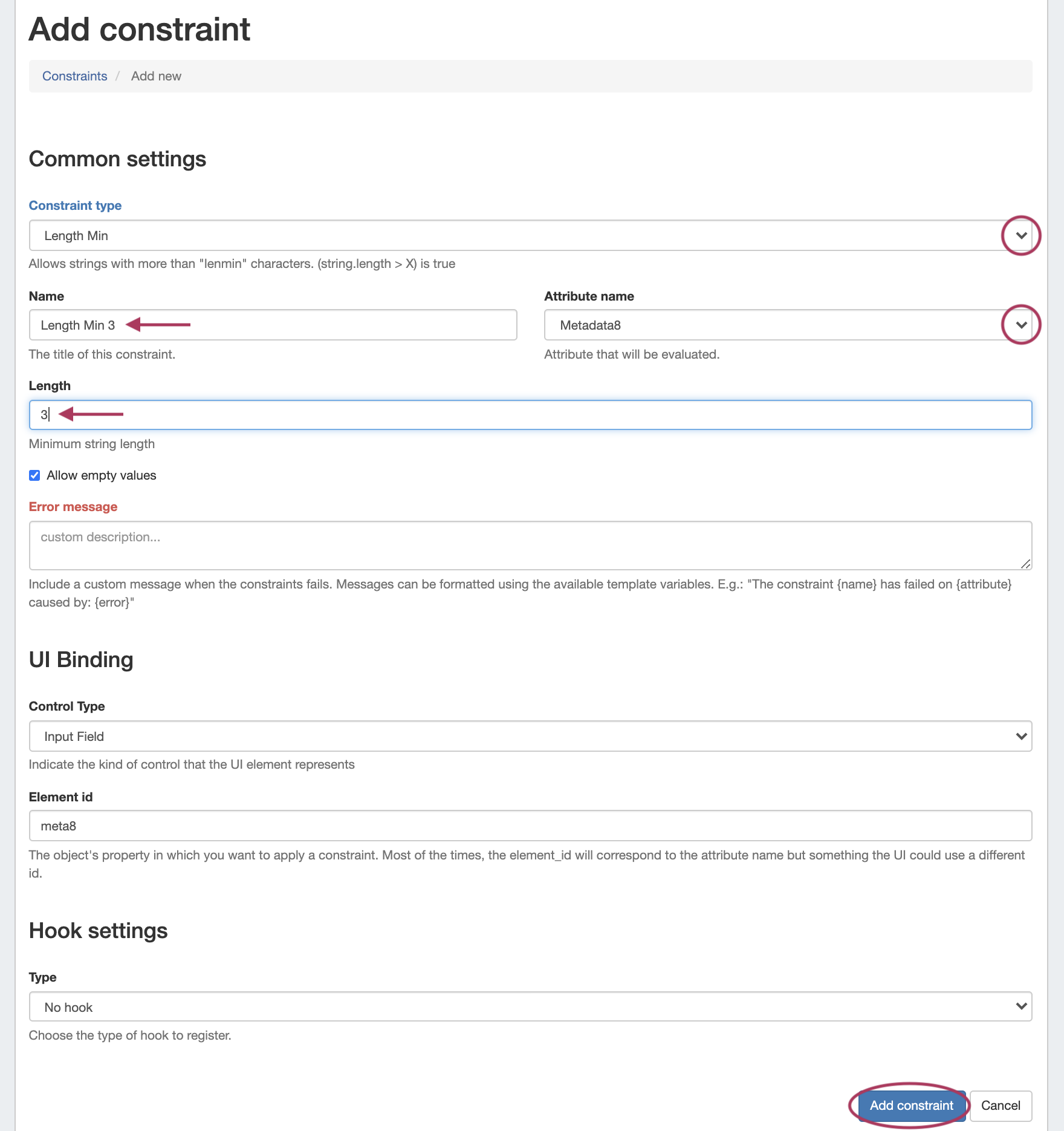
To add a new Constraint, click "Add Constraint"
In the "Add Constraint" screen, select (at mimimum, depending on the selected constraint type):
- The constraint type (here, "Length Min")
- The name for the constraint
- The attribute (IPAM Field) on which to apply the constraint
- Constraint specific comparison values, here as "Length"
- Select whether to allow empty values in the attribute field
If desired, you may enter a custom error message, customize the UI binding (although it it automatically filled in if you select a standard IPAM Attribute), or add an event hook setting.
When done, click "Add Constraint" to save.
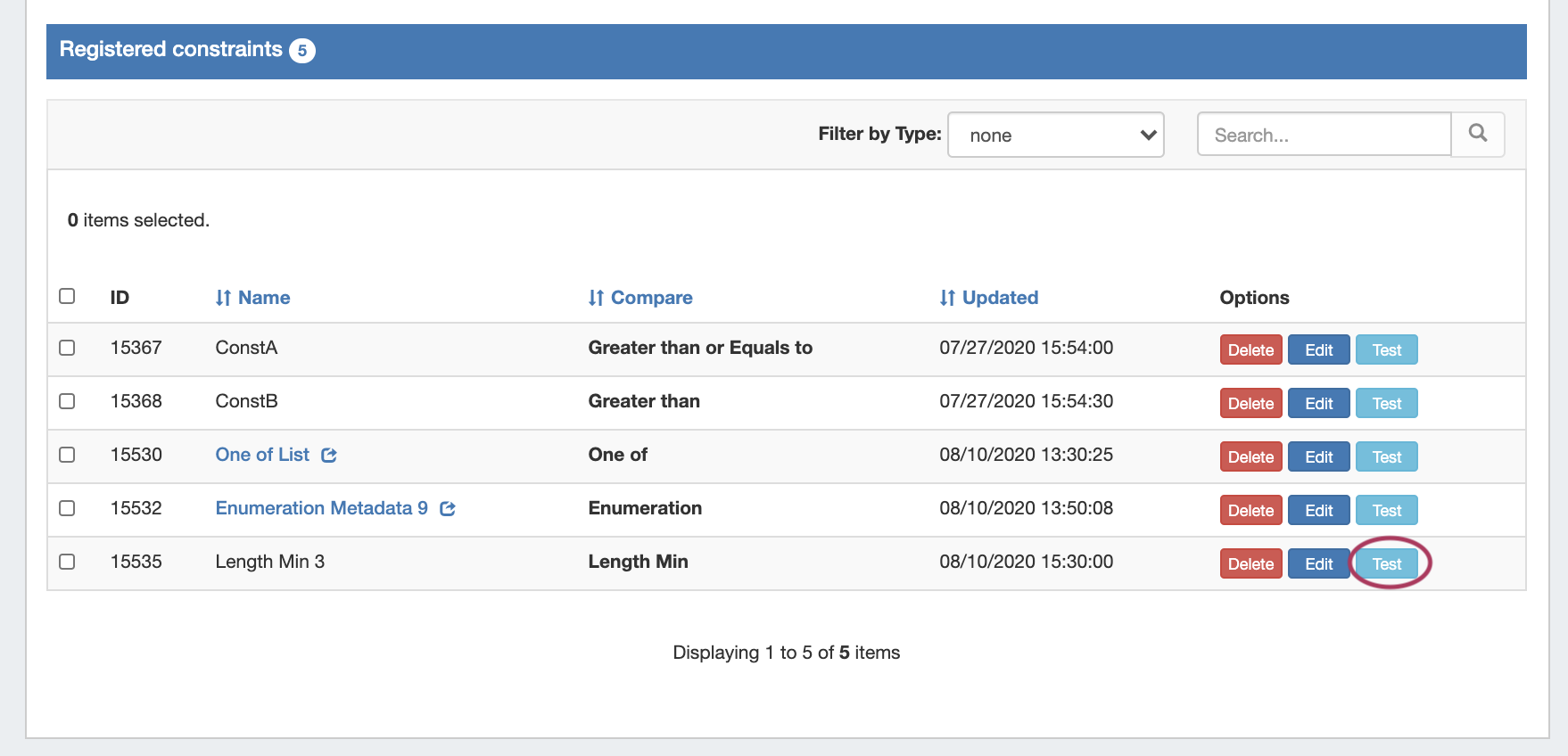
Test Constraint
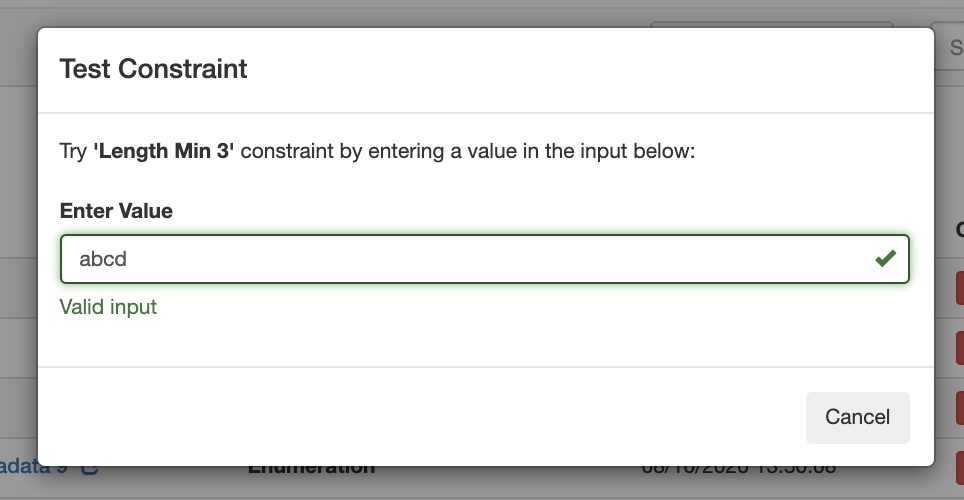
To test a Constraint, click "Test".
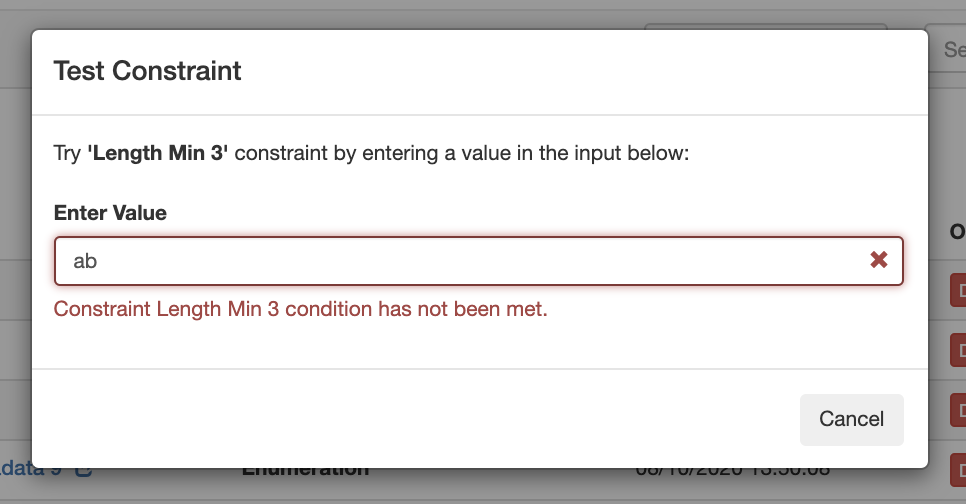
The test constraint form will appear - enter a test value, and you can check whether the constraint returns an appropriate invalid or valid response:
Invalid result, for "Length Min 3":
Valid result, for "Length Min 3":
Edit Constraint
To edit a Constraint, click "Edit". The constraint details will open, matching the "Add Constraint" form.
Adjust values or settings as desired, and then click "Update Constraint".
Delete Constraint
To delete a Constraint, click "Delete".
A Confirmation box will appear - confirm whether to delete the constraint, or click "Close" to exit without deletion.
Working with Constraints in IPAM Manage
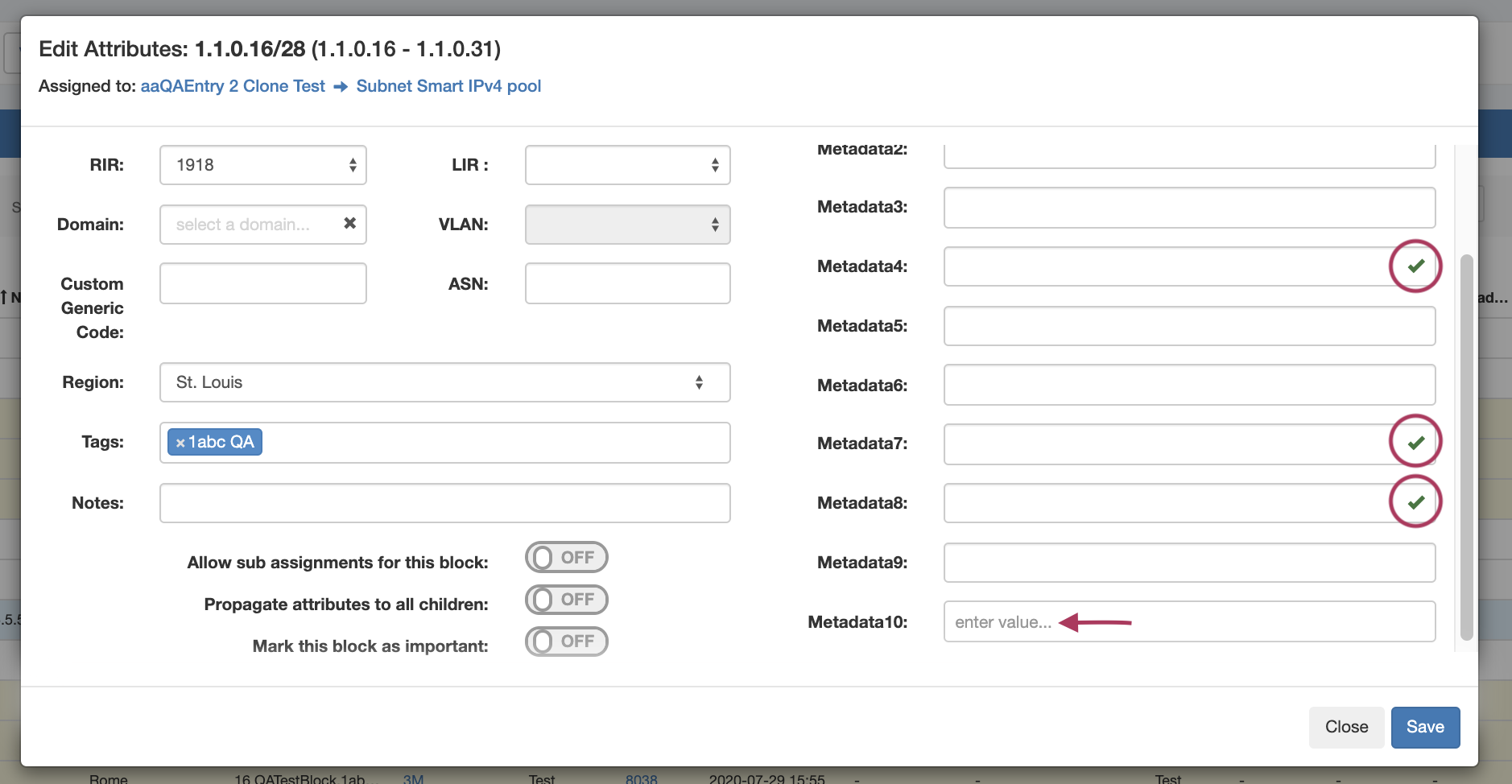
When a field is viewed in IPAM Manage that has a constraint applied, a "check" icon will display next to the field input for simple input constraint checks, if empty values are allowed.
If the constraint is of a type that has been set up with a dropdown box, then the dropdown box and placeholder text will be applied:
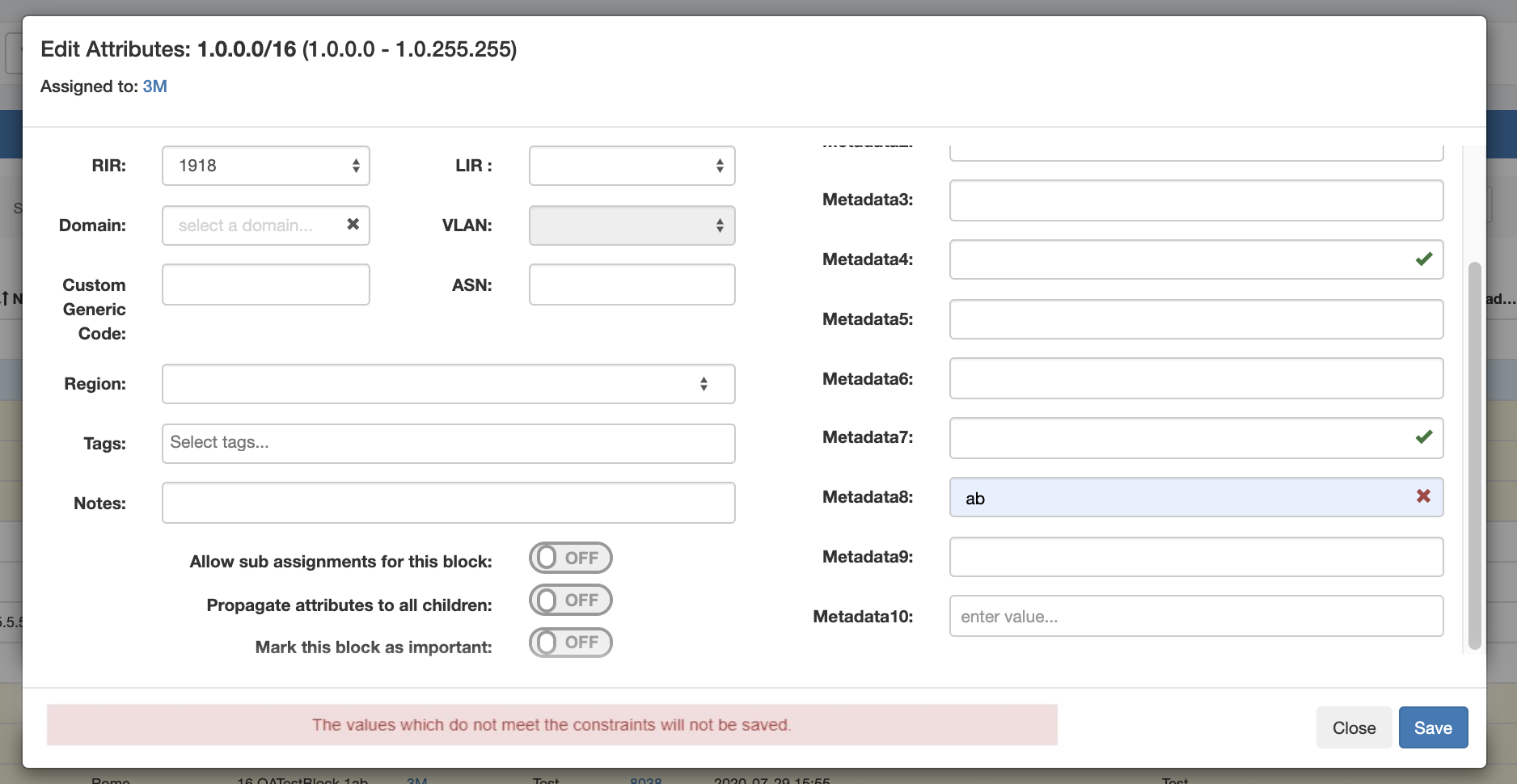
In this example, constraint validation checks have been applied to Metadata4, Metadata7, and Metadata8, with a dropdown "One Of" constraint applied to Metadata 10.
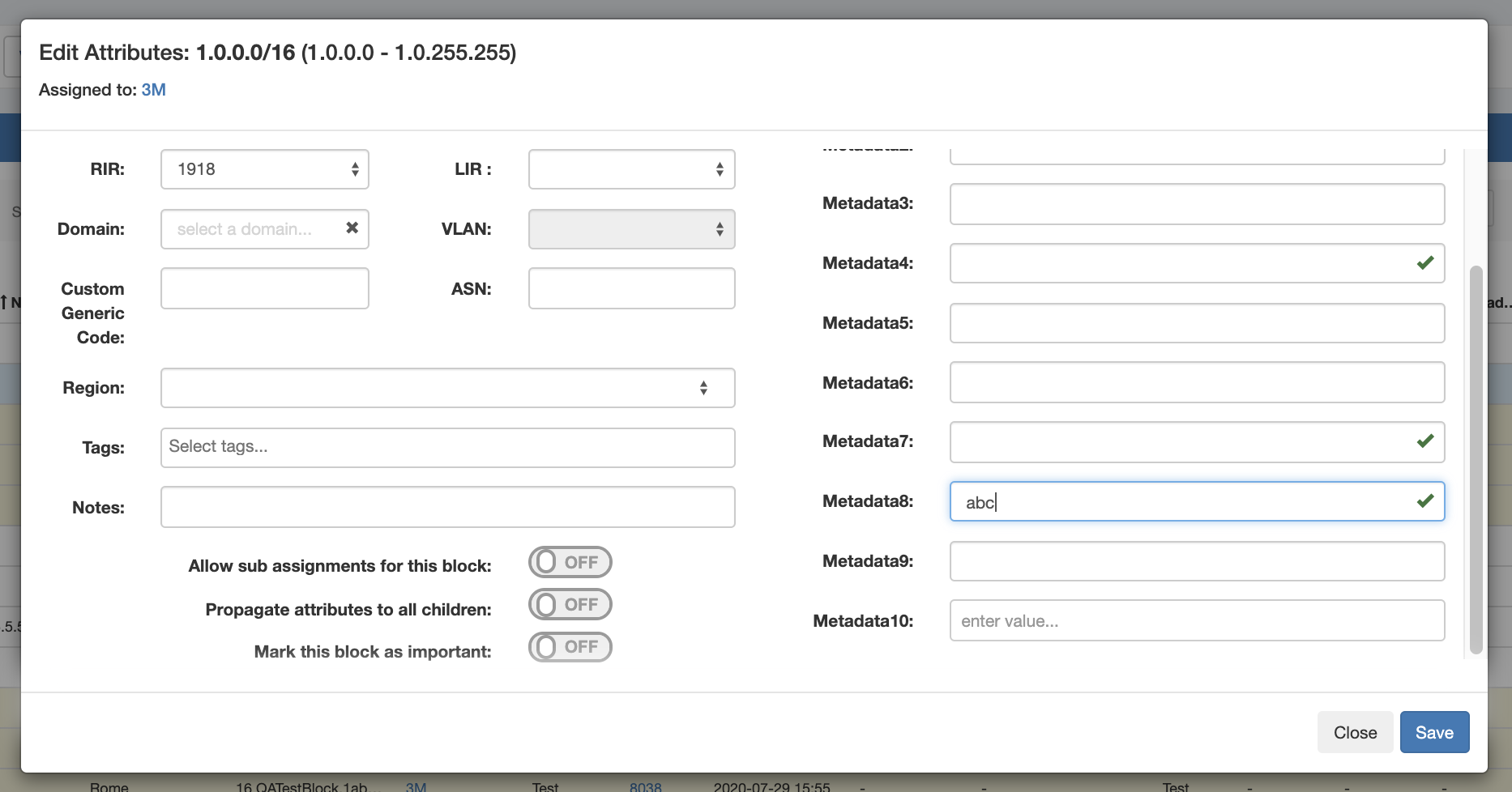
Metadata8 has been associated with our previous constraint example, "Length Min 3", so if we enter less than three characters into that field, we should get an error, and see the "X" for the input not meeting the constraint settings:
On the other hand, a valid input will return to displaying the "valid" success checkmark: