Workflow Options
...
This section details out options the tabs available under a Workflow step - Inputs (Required / Optional), Iteration, Sub Steps, Conditions, and Output, accessed by clicking on the header bar for any workflow step.
User Inputs
User Inputs are configured for a step under the "Required Inputs" and/or "Optional Inputs" tabs under a workflow:
...
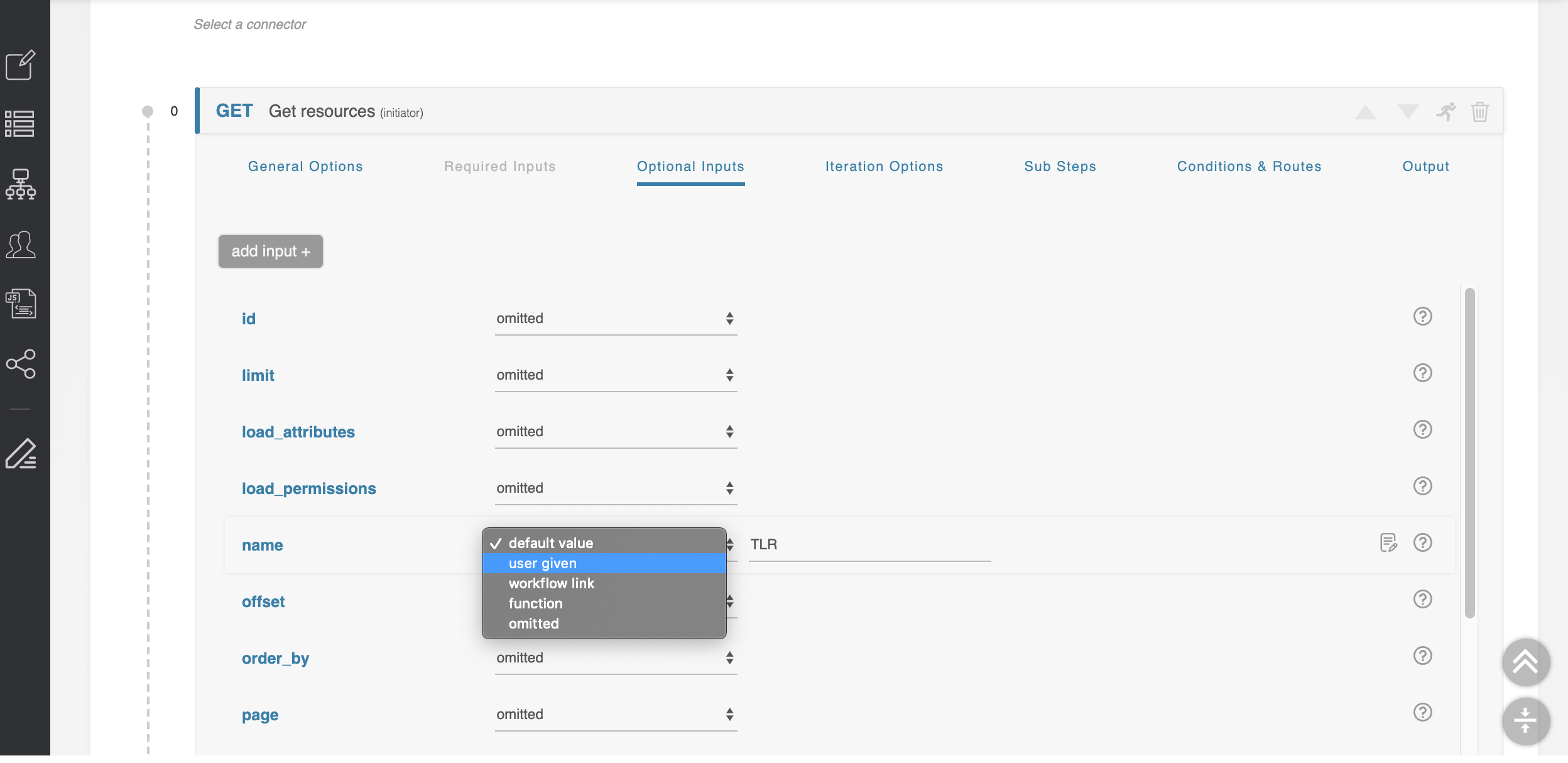
The ‘Optional Inputs’ section contains those parameters that the API call might make use of which are not explicitly required. Some APIs are flexible and allow you to add additional optional parameters not explicitly defined in the API specification. To allow for this, the ‘add input’ button lets you define an arbitrary optional inputs to complete the API call.
Working with Inputs
All types of inputs have a small ‘?’ to the right of their input area which will supply help text as to what that parameter does. For more details, see the official API documentation for the API service you are using.
...
- Omitted: The default state. This parameter will not be sent with the API call. This option is not available for 'required' parameters.
- Default value: This parameter will be set to some constant, defined here.
- User given: This parameter will be supplied by the user executing the ACP Workflow.
- Workflow link: The input for this parameter is the output of another step. For details, see Workflow Steps → Links Between Steps (Workflow Links).
- Iteration: This parameter becomes available when the Iteration Options section is configured. Inputs set to ‘iteration’ are populated with the iterated run number, starting from zero. For detail, see Initiator Conditions and Iteration.
- Function: The input of this parameter will be supplied by the output of a javascript function. For detail, see Javascript Functions.
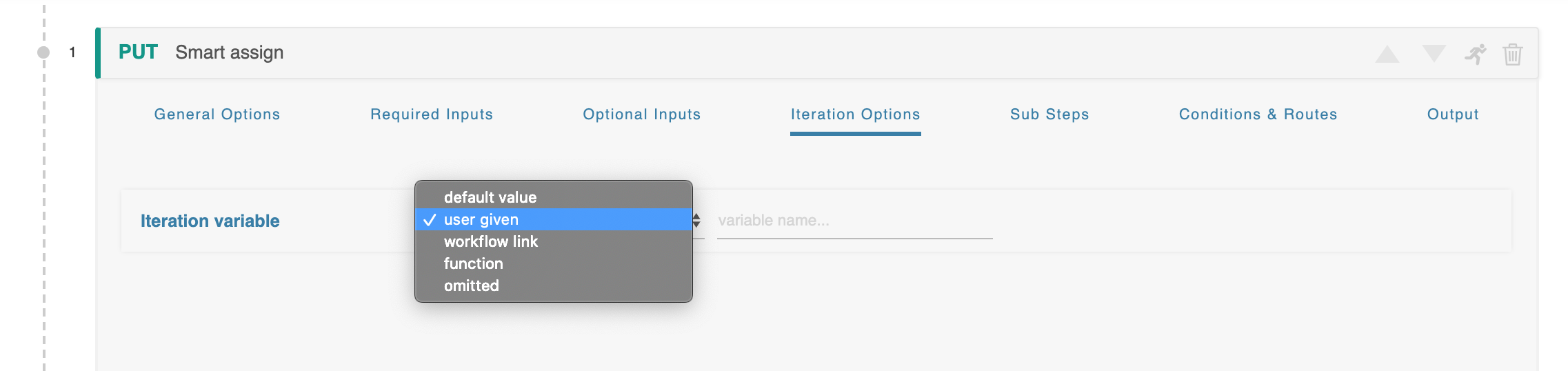
Iteration Options
When using an iteration variable, it can be customized with the same options as any other input.
...
When the ‘user given’ option is selected the form changes to show an additional field where this variable can be named. These variable names are global in scope, and the same name used multiple times will refer to the same variable. For example if your variable is ‘customer_name’ and it is used in three separate steps, the workflow will only request ‘customer_name’ once and use it in all three instances.
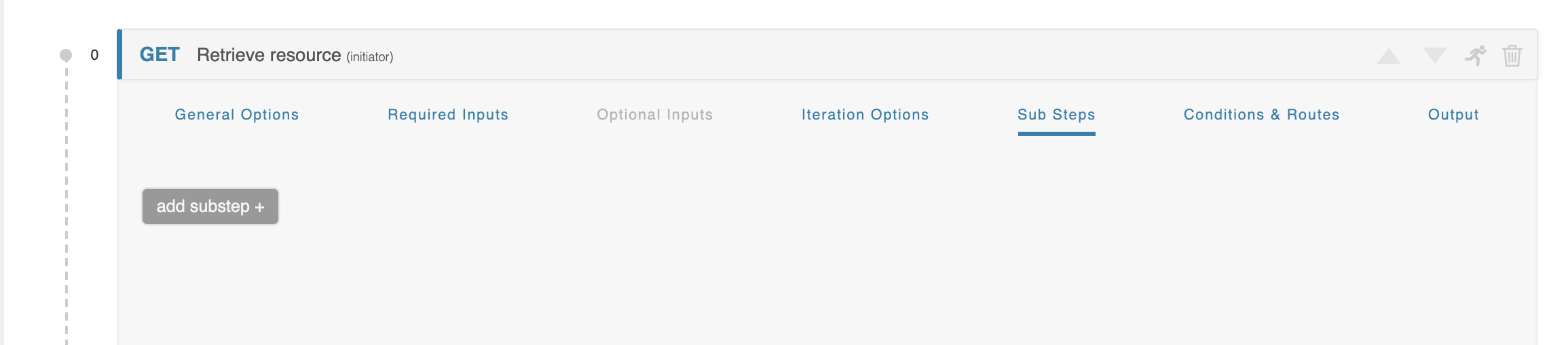
Sub-Steps
Each Workflow Step has an optional Sub-steps section. This area is initially empty, but can be populated with sub-steps to create a Workflow within a Workflow.
...
Each Inner Workflow can have, if needed, Sub-steps of is own, creating an Inner-Inner Workflow. There is no limit to how many Workflows deep this can go.
Conditions and Routing
The ‘Conditions & Routes’ section examines the data returned as the result of a workflow step and decides which step is next. The workflow creator can define an unlimited number of separate conditions leading to different next steps, and each condition can consist of an unlimited number of individual comparisons. The system evaluates each condition in order, from top to bottom, and immediately proceeds when it finds a match.
...
Each routing section is evaluated in order, from top to bottom, until a match is found. Once a match is found the system proceeds to the indicated step without evaluating further conditions. Multiple matches are not checked for. If no next-route is found, the workflow errors, possibly triggering a rollback.
Values
Initially, each condition consists of a single comparison clause. All comparison clauses consist of a ‘left value,’ which indicates source data, an ‘operator,’ which defines the nature of the comparison, and a ‘right value,’ which denotes the comparison data.
...
- http code: uses the HTTP code returned by the API call in the step.
- body: accesses some value in the body of the API request. Parameters are accessed by name, and arrays are accessed by “$index.parameter” as elsewhere. (ex: the name of the first object in an array would be ‘0.name’)
- default value: a static, default value defined by the workflow creator
- user given: a value which must be supplied when the workflow is invoked
- workflow link: a reference to data obtained in a previous step
- function: indicates that the data for this field is the output of a data-processing function. These functions are described in greater detail later in this document.
Operators
The ‘operators’ are self-explanatory boolean comparators, but a few require special syntax:
- The operators IN and NOT IN accept comma-separated arrays (ex: one,two,three) for their values. See “Getting Started 8. Compound Branching Conditions” for examples.
- NULL, NOT NULL, TRUE, and FALSE do not require a right-hand value.
- BETWEEN and NOT BETWEEN accept a tuple with the format “minvalue,maxvalue” (ex: ‘200,299’ for valid HTTP codes).
Additional Conditions
The add-clause button (the plus symbol) and the remove-clause button (the minus symbol) on the far right allow you to join individual clauses into a compound clause, like “if A or B” or “if A and B and C”. Once clicked, the add clause button creates a new clause below the last existing clause.
At the far right of each comparison clause is a drop down that dictates how this and the next clause are to be joined. The drop-down contains two operators, AND and OR, which join the two conditions as advertised.
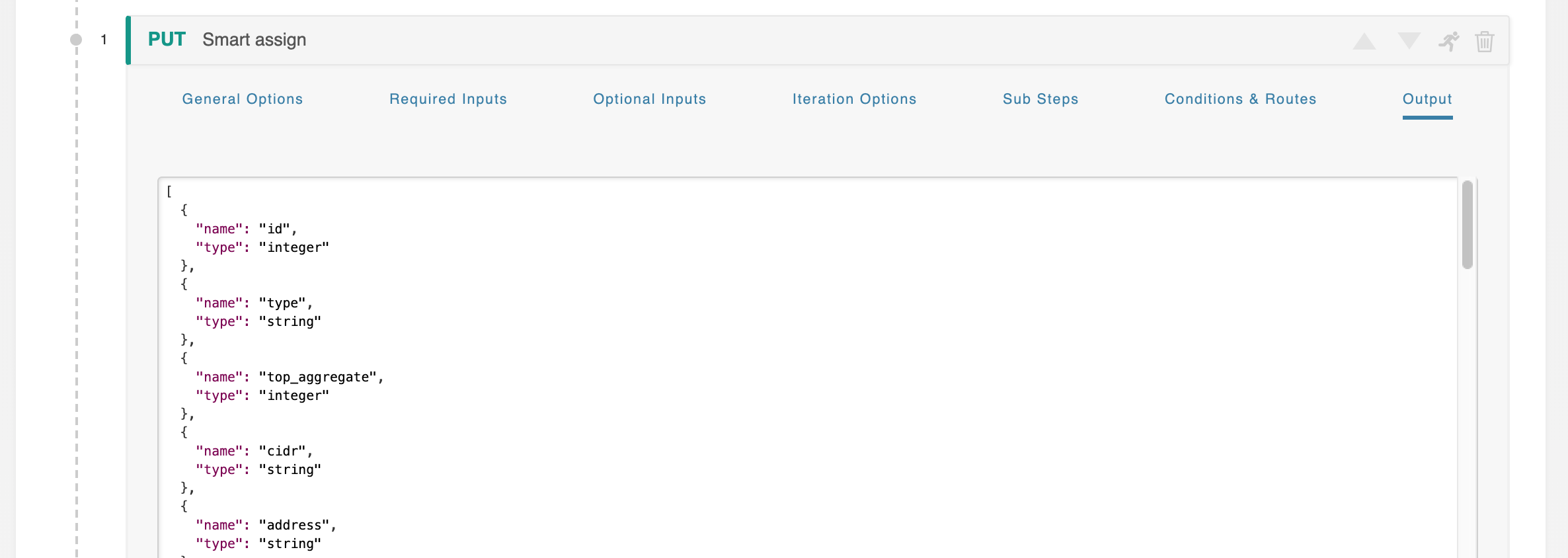
Step Output
Step Output displays an example of the output that will be generated when executing the step.
Additional Information
Continue on to additional User Guide pages for detailed information on working in ACP:
ACP User Guide
Children Display depth 1 page ACP User Guide
...